Trigger pipelines by using the API
- Tier: Free, Premium, Ultimate
- Offering: GitLab.com, GitLab Self-Managed, GitLab Dedicated
To trigger a pipeline for a specific branch or tag, you can use an API call to the pipeline triggers API endpoint.
If you are migrating to GitLab CI/CD, you can trigger GitLab CI/CD pipelines by calling the API endpoint from the other provider's jobs. For example, as part of a migration from Jenkins or CircleCI.
When authenticating with the API, you can use:
- A pipeline trigger token to trigger a branch or tag pipeline with the pipeline triggers API endpoint.
- A CI/CD job token to trigger a multi-project pipeline.
- Another token with API access to create a new pipeline with the project pipeline API endpoint.
Create a pipeline trigger token
You can trigger a pipeline for a branch or tag by generating a pipeline trigger token and using it to authenticate an API call. The token impersonates a user's project access and permissions.
Prerequisites:
- You must have at least the Maintainer role for the project.
To create a trigger token:
- On the left sidebar, select Search or go to and find your project.
- Select Settings > CI/CD.
- Expand Pipeline trigger tokens.
- Select Add new token
- Enter a description and select Create pipeline trigger token.
- You can view and copy the full token for all triggers you have created.
- You can only see the first 4 characters for tokens created by other project members.
It is a security risk to save tokens in plain text in public projects, or store them in a way that malicious users could access them. A leaked trigger token could be used to force an unscheduled deployment, attempt to access CI/CD variables, or other malicious uses. Masked CI/CD variables help improve the security of trigger tokens. For more information about keeping tokens secure, see the security considerations.
Trigger a pipeline
After you create a pipeline trigger token, you can use it to trigger pipelines with a tool that can access the API, or a webhook.
Use cURL
You can use cURL to trigger pipelines with the pipeline triggers API endpoint. For example:
-
Use a multiline cURL command:
curl --request POST \ --form token=<token> \ --form ref=<ref_name> \ "https://gitlab.example.com/api/v4/projects/<project_id>/trigger/pipeline" -
Use cURL and pass the
<token>and<ref_name>in the query string:curl --request POST \ "https://gitlab.example.com/api/v4/projects/<project_id>/trigger/pipeline?token=<token>&ref=<ref_name>"
In each example, replace:
- The URL with
https://gitlab.comor the URL of your instance. -
<token>with your trigger token. -
<ref_name>with a branch or tag name, likemain. -
<project_id>with your project ID, like123456. The project ID is displayed on the project overview page.
Use a CI/CD job
You can use a CI/CD job with a pipeline trigger token to trigger pipelines when another pipeline runs.
For example, to trigger a pipeline on the main branch of project-B when a tag
is created in project-A, add the following job to project A's .gitlab-ci.yml file:
trigger_pipeline:
stage: deploy
script:
- 'curl --fail --request POST --form token=$MY_TRIGGER_TOKEN --form ref=main "${CI_API_V4_URL}/projects/123456/trigger/pipeline"'
rules:
- if: $CI_COMMIT_TAG
environment: productionIn this example:
-
1234is the project ID forproject-B. The project ID is displayed on the project overview page. - The
rulescause the job to run every time a tag is added toproject-A. -
MY_TRIGGER_TOKENis a masked CI/CD variable that contains the trigger token.
Use a webhook
To trigger a pipeline from another project's webhook, use a webhook URL like the following for push and tag events:
https://gitlab.example.com/api/v4/projects/<project_id>/ref/<ref_name>/trigger/pipeline?token=<token>Replace:
- The URL with
https://gitlab.comor the URL of your instance. -
<project_id>with your project ID, like123456. The project ID is displayed on the project overview page. -
<ref_name>with a branch or tag name, likemain. This value takes precedence over theref_namein the webhook payload. The payload'srefis the branch that fired the trigger in the source repository. You must URL-encode theref_nameif it contains slashes. -
<token>with your pipeline trigger token.
Access webhook payload
If you trigger a pipeline by using a webhook, you can access the webhook payload with
the TRIGGER_PAYLOAD predefined CI/CD variable.
The payload is exposed as a file-type variable,
so you can access the data with cat $TRIGGER_PAYLOAD or a similar command.
Pass CI/CD variables in the API call
You can pass any number of CI/CD variables in the trigger API call, though using inputs to control pipeline behavior offers improved security and flexibility over CI/CD variables.
These variables have the highest precedence, and override all variables with the same name.
The parameter is of the form variables[key]=value, for example:
curl --request POST \
--form token=TOKEN \
--form ref=main \
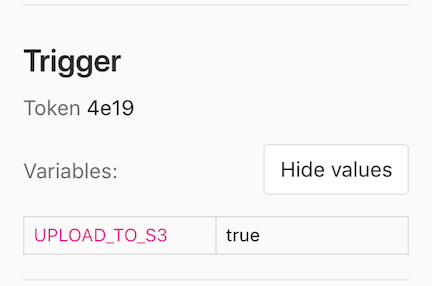
--form "variables[UPLOAD_TO_S3]=true" \
"https://gitlab.example.com/api/v4/projects/123456/trigger/pipeline"CI/CD variables in triggered pipelines display on each job's page, but only users with the Owner and Maintainer role can view the values.
Using inputs to control pipeline behavior offers improved security and flexibility over CI/CD variables.
Pass pipeline inputs in the API call
You can pass pipeline inputs in the trigger API call. Inputs provide a structured way to parameterize your pipelines with built-in validation and documentation.
The parameter format is inputs[name]=value, for example:
curl --request POST \
--form token=TOKEN \
--form ref=main \
--form "inputs[environment]=production" \
"https://gitlab.example.com/api/v4/projects/123456/trigger/pipeline"Input values are validated according to the type and constraints defined in your pipeline's
spec:inputs section:
spec:
inputs:
environment:
type: string
description: "Deployment environment"
options: [dev, staging, production]
default: devRevoke a pipeline trigger token
To revoke a pipeline trigger token:
- On the left sidebar, select Search or go to and find your project.
- Select Settings > CI/CD.
- Expand Pipeline triggers.
- To the left of the trigger token you want to revoke, select Revoke ({remove}).
A revoked trigger token cannot be added back.
Configure CI/CD jobs to run in triggered pipelines
To configure when to run jobs in triggered pipelines, you can:
- Use
ruleswith the$CI_PIPELINE_SOURCEpredefined CI/CD variable. - Use
only/exceptkeywords, thoughrulesis the preferred keyword.
$CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE value |
only/except keywords |
Trigger method |
|---|---|---|
trigger |
triggers |
In pipelines triggered with the pipeline triggers API by using a trigger token. |
pipeline |
pipelines |
In multi-project pipelines triggered with the pipeline triggers API by using the $CI_JOB_TOKEN, or by using the trigger keyword in the CI/CD configuration file. |
Additionally, the $CI_PIPELINE_TRIGGERED predefined CI/CD variable is set to true
in pipelines triggered with a pipeline trigger token.
See which pipeline trigger token was used
You can see which pipeline trigger token caused a job to run by visiting the single job page. A part of the trigger token displays on the right sidebar, under Job details.
In pipelines triggered with a trigger token, jobs are labeled as triggered in
Build > Jobs.
Troubleshooting
403 Forbidden when you trigger a pipeline with a webhook
When you trigger a pipeline with a webhook, the API might return a {"message":"403 Forbidden"} response.
To avoid trigger loops, do not use pipeline events to trigger pipelines.
404 Not Found when triggering a pipeline
A response of {"message":"404 Not Found"} when triggering a pipeline might be caused
by using a personal access token
instead of a pipeline trigger token. Create a new trigger token
and use it instead of the personal access token.
The requested URL returned error: 400 when triggering a pipeline
If you attempt to trigger a pipeline by using a ref that is a branch name that
doesn't exist, GitLab returns The requested URL returned error: 400.
For example, you might accidentally use main for the branch name in a project that
uses a different branch name for its default branch.
Another possible cause for this error is a rule that prevents creation of the pipelines when CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE value is trigger, such as:
rules:
- if: $CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "trigger"
when: neverReview your workflow:rules to ensure a pipeline can be created when CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE value is trigger.